Mitopure vs CoQ10 for skin
Combat aging, boost collagen, and enhance skin hydration. Let’s take a look at what CoQ10 does for our cells and how it compares with Mitopure®.
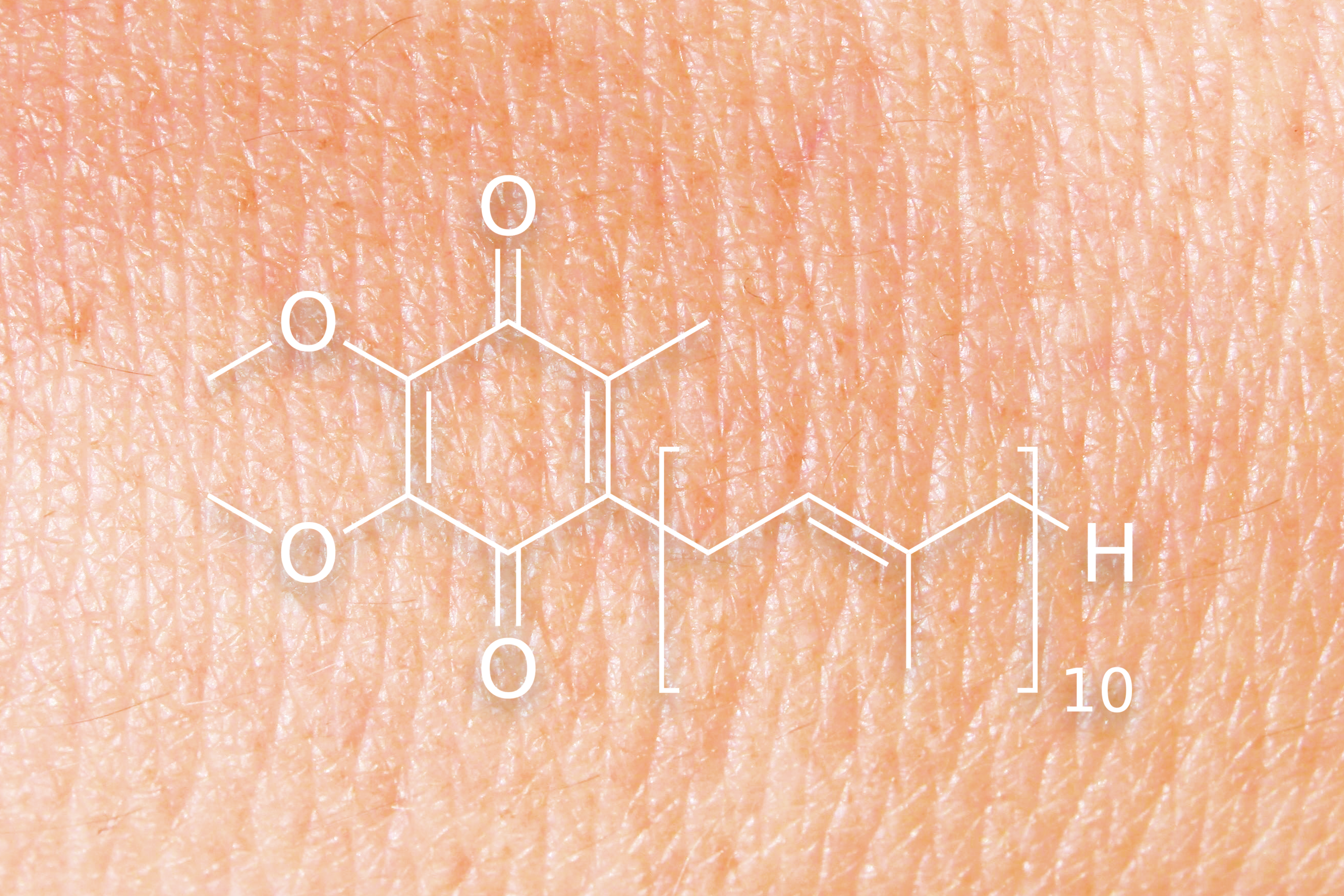
What to know
While CoQ10 and Mitopure are both used to support mitochondrial health and skin health
Clincal trials with CoQ10 are lacking as compared to those done with Mitopure
Topical application of Mitopure® promotes skin elasticity, reduces wrinkles, and evens out skin tone
Your body is always working. We are in constant need of various nutrients that keep our cells nourished and healthy! Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is one such critical nutrient. Many are familiar with the health effects of CoQ10 in the body, but there are also benefits of CoQ10 for skin health and appearance. Let’s delve into this lesser-known application of CoQ10 for skin and see how it compares to Mitopure® (Urolithin A).
Science behind CoQ10 for skin
CoQ10 is an antioxidant naturally found in the mitochondria of our cells. The compound uses its antioxidant properties to battle free radicals which cause oxidative damage, a major aging contributor. CoQ10 fends off free radicals, preventing them from wreaking havoc on the cell.
As we age, our need for antioxidant protection increases for two primary reasons:
- Mitochondrial dysfunction. Factors like mitochondrial genomic damage and insufficient mitophagy lead to mitochondrial dysfunction. This reduces the efficiency of cellular respiration (i.e., energy producing reactions performed in the mitochondria), increasing the production of free radicals. Free radicals induce oxidative damage in the mitochondria and cells, accelerating aging. Keep in mind that mitochondrial dysfunction is one of the hallmarks of aging.[1]
- Antioxidant depletion. CoQ10 and other antioxidants in the skin and body diminish with age. CoQ10 is unable to keep up with the rising levels of free radicals. More and more oxidative damage accumulates within the mitochondria and cells, resulting in accelerated aging of the skin and body.[2]
With so many skincare options available, it can be overwhelming to confidently choose a product that truly works for you. While both CoQ10 and Mitopure® are marketed for their potential to target aging skin, it's important to drill down into what the science really says.
CoQ10 vs Mitopure®
While antioxidants are great for mitochondria and skin health, they don’t address a significant cause of free radical generation. In the same way zombie cells need to be cleared out of our bodies, dysfunctional mitochondria need to be cleared out and replaced. Without that quality control (i.e., mitophagy), we accumulate too many dysfunctional mitochondria, which results in excessive free radical production.
CoQ10 has antioxidant properties that help fight free radicals, but its ability to improve skin health is not well-documented in human trials.
Mitopure®, on the other hand, has several clinical trials proving it’s benefits.
Let’s compare the two.

The Serum
Bestseller4.6 · 129 reviews
Lifts the skin. Powered by Mitopure®
5 skin benefits: Mitopure vs CoQ10
Like Mitopure®, topically applied CoQ10 skin care is known to promote skin health at the cellular level; however, unlike Mitopure, many of the CoQ10 skin benefits have yet to be proven in human clinical trials.[3]
Enhance skin elasticity and firmness
As we age, collagen levels decline. Skin collagen levels are a critical biomarker of skin health and longevity. A strong collagen scaffold in the skin maintains structural integrity, keeping the skin firm and lifted. The scaffold also keeps pores taut and small, promoting skin elasticity and a smooth skin texture.[4]
Mitopure® is clinically proven to promote collagen organization and assembly to increase[5] firmness and elasticity, which differentiates it from CoQ10.[6]

Reduce photoaging
Sun exposure is responsible for 80% of visible facial skin aging.[7] Some animal studies suggest that CoQ10 may be able to reduce photodamage and slow photoaging.[9] Mitopure®, on the other hand, is clinically proven to reduce sun sensitivity in the skin to protect against photoaging.
Reduce wrinkles and fine lines
One placebo-controlled clinical trial with CoQ10 showed an improvement in wrinkles, but it was after five months of use. [8]In a world where we are looking for fast results, this seems like an awful long time. Mitopure works much more quickly - clinical trials saw visible improvements in fine lines and wrinkles in just two weeks!

Improve skin hydration
A strong collagen scaffold can shrink down pores and also form a thicker skin barrier. This improves our skin’s ability to keep aggressors out while locking moisture in. It also visibly improves skin texture and hydration. Well-hydrated skin appears plump, smooth, and healthy.
Limited data exists on CoQ10’s ability to improve skin hydration, whereas clinical trials with Timeline’s Skincare line showed dramatic improvements in skin hydration. Remember, it’s especially important to keep your skin hydrated during the dryer months of the year!
Even-out skin tone
Uneven skin tone and sun spots are often triggered by sun exposure or hormonal imbalance. CoQ10 can inhibit the production of melanin, a biological pigment. This gives the compound a depigmenting property. [9]Conditions such as hyperpigmentation and melasma could potentially be addressed with CoQ10 products. Regular use of CoQ10 can contribute to a more even and radiant skin tone over time.
Mitopure® encourages the repair and regeneration of the skin at the cellular level. Our trials have demonstrated people using Timeline Skincare products report noticeable improvements in dark spots, discoloration and blemishes.
How to use CoQ10 for skin health
Now that we see the myriad of ways CoQ10 can improve skin health let’s look at how we can incorporate a CoQ10 supplement for skin into our routine.
What to look for in skincare products
When it comes to finding a CoQ10 supplement for skin, the formulation must be considered to ensure maximum penetration to all layers of the skin. Be cautious about using products with harsh ingredients such as synthetic dyes and fragrances, as these may counteract the positive effects of CoQ10 and damage the skin.
When and how to use CoQ10
CoQ10 can be used in both morning and evening skincare routines and can be used with other topical products. It tends to be well-tolerated by most people, even those with sensitive skin.
Alternatives to CoQ10
The majority of CoQ10's benefits come from its ability to act as an antioxidant. However, most of the research to date has been done on animals or in cell tests, not real-life applications on human skin. This is where exploring alternatives becomes essential. Ingredients like Urolithin A stand out because they are specifically designed for human skin, offering a blend of scientific rigor and practical benefits. It's a way to ensure your skincare is not just promising but truly effective.

Urolithin A as a CoQ10 alternative
Mitopure®, our patented highly pure form of the Urolithin A compound, has recently surfaced as a healthy aging molecule that promotes skin health at the cellular level. Mitopure® addresses the root cause of why skin ages.
Mitopure is clinically proven to:
- Increase firmness and elasticity
- Reduce the appearance of fine lines & wrinkles
- Increase radiance for a healthy glow
All of the Timeline Skincare products contain Mitopure®. Along with the slew of benefits, Mitopure® is also exceptionally safe for sensitive skin. This makes it a suitable and highly effective CoQ10 alternative for your skin!

The Day Cream
4.6 · 91 reviews
Redensifies the skin's appearance. Powered by Mitopure®
Final thoughts
While CoQ10 has its merits, especially in antioxidant protection, Mitopure® shines with its clinically proven, fast-acting benefits. From enhancing skin firmness and elasticity to reducing wrinkles and improving hydration, Mitopure® not only tackles the signs of aging at the surface but also rejuvenates skin at a cellular level. So, if you're looking for a product that truly works, Mitopure® is the clear choice for keeping your skin vibrant and youthful.
Authors

Freelance writer

Reviewed by
Lead Regulatory Affairs & Scientific Manager Alliances at Timeline
References
- ↑
López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013 Jun 6;153(6):1194-217. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.039. PMID: 23746838; PMCID: PMC3836174.
- ↑
Barcelos IP, Haas RH. CoQ10 and Aging. Biology (Basel). 2019 May 11;8(2):28. doi: 10.3390/biology8020028. PMID: 31083534; PMCID: PMC6627360.
- ↑
Ayunin Q, Miatmoko A, Soeratri W, Erawati T, Susanto J, Legowo D. Improving the anti-ageing activity of coenzyme Q10 through protransfersome-loaded emulgel. Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 18;12(1):906. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-04708-4. PMID: 35042910; PMCID: PMC8766480.
- ↑
Al-Atif H. Collagen Supplements for Aging and Wrinkles: A Paradigm Shift in the Fields of Dermatology and Cosmetics. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2022 Jan 1;12(1):e2022018. doi: 10.5826/dpc.1201a18. PMID: 35223163; PMCID: PMC8824545.
- ↑
Ayunin, Q., Miatmoko, A., Soeratri, W. et al. Improving the anti-ageing activity of coenzyme Q10 through protransfersome-loaded emulgel. Sci Rep 12, 906 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-04708-4
- ↑
Topical application of Urolithin A slows intrinsic skin aging and protects from UVB-mediated photodamage: Findings from Randomized Clinical Trials D D’Amico, AM Fouassier, J Faitg, N Hennighausen, M Brandt, D Konstantopoulos, C Rinsch, A Singh medRxiv 2023.06.16.23291378; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.16.23291378
- ↑
Flament F, Bazin R, Laquieze S, Rubert V, Simonpietri E, Piot B. Effect of the sun on visible clinical signs of aging in Caucasian skin. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013 Sep 27;6:221-32. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S44686. PMID: 24101874; PMCID: PMC3790843.
- ↑
Inui M, Ooe M, Fujii K, Matsunaka H, Yoshida M, Ichihashi M. Mechanisms of inhibitory effects of CoQ10 on UVB-induced wrinkle formation in vitro and in vivo. Biofactors. 2008;32(1-4):237-243. doi:10.1002/biof.5520320128
- ↑
Zhang M, Dang L, Guo F, Wang X, Zhao W, Zhao R. Coenzyme Q(10) enhances dermal elastin expression, inhibits IL-1α production and melanin synthesis in vitro. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2012 Jun;34(3):273-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2494.2012.00713.x. Epub 2012 Mar 24. PMID: 22339577.

•
Skincare•
Inside Timeline’s Lab: Meet Mitochondria Expert Julie Faitg

•








