NAD+ IV drips: Are they worth it?
NAD+ IV drips are one of the newest trends in anti-aging and health. Learn about the potential benefits and risks and decide if it's worth it.
With IV “bars” popping up in health-conscious cities around the country, you may have noticed offerings for NAD IV therapy. Often these treatments come with claims to boost your energy, clear brain fog, promote longevity, and the list goes on.
While NAD IV therapy may sound tempting, it can be expensive. So you may be wondering, are NAD drips worth it, and are they safe? And how do they compare with other energy-boosting supplements?
We’ll break down the pros and cons so that you can decide if the NAD+ IV therapy benefits are worth it for you.
NAD+ Molecule Structure
What is NAD+
NAD (sometimes referred to as NAD+) stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. This molecule is naturally present in all of our cells, participating in many vital biological processes, including energy metabolism.

As we age, our NAD levels decrease, and this decline is associated with several age-related chronic conditions, including cancer and neurodegenerative disease. Studies have shown that supporting NAD metabolism can help to prevent the fall of NAD levels and may be beneficial in the fight against diseases associated with aging.[1]
Role of NAD+
The role of NAD+ in energy metabolism is one of the molecule's many important functions. Here, NAD+ acts as an electron donor, shuttling hydrogen molecules back and forth. When NAD+ accepts a hydrogen molecule, it becomes NADH. When that hydrogen molecule gets donated, it returns to NAD+. This process repeats, building an energy gradient that ultimately generates ATP, our body’s energy source.
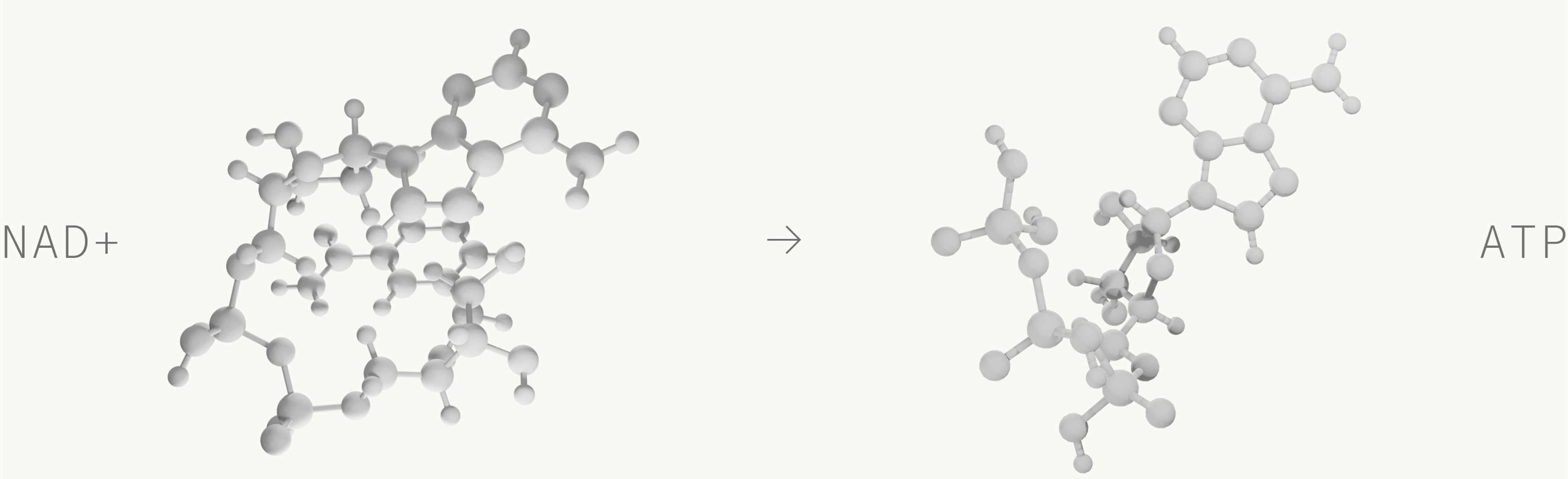
NAD is involved in other cellular processes as well. [2]This includes:
- DNA repair
- Cellular senescence (the process by which cells age)
- Immune function
About NAD+ IV Therapy
During NAD+ IV therapy, NAD+ is mixed with saline, and it is slowly administered through the vein. Proponents of IV treatments say that directly supplying NAD to the bloodstream allows it to move quickly to the cells, where it can get to work. However, a small pilot study showed that it took 2 hours for blood levels to rise, reaching its peak at six hours.[3]
This does not mean that IV NAD lacks benefits. Research suggests that boosting NAD levels by any method (IV, oral supplements, or lifestyle approaches like fasting and exercise)[4] may be able to improve your health.[5] Presently, it is unclear, however, which method works the best.
Benefits of NAD+ Drips
Advocates of NAD+ drips claim the treatment has a number of benefits, but the truth is that there are limited studies looking specifically at IV administration of NAD+. Much of the research done around the benefits of boosting NAD+ levels comes from the use of NAD+ precursors.[6]
Let’s examine five of the claims made surrounding NAD infusion benefits:
1. Slows aging - It is well established that NAD levels decline with age. This is a fact that has prompted longevity researchers to look into the specific role that NAD plays in aging. In yeast and mouse models boosting NAD levels with NAD precursors was able to extend lifespan and slow down the progression of age-related conditions.[7] We don’t yet know if this translates into humans or if similar results would be seen with NAD infusions, but these preclinical trials are promising.
2. Boosting energy - Since NAD is a key player in energy metabolism, it makes sense that boosting NAD levels would boost your energy levels. While limited clinical studies have shown that NAD drips improve energy, boosting NAD levels through dietary supplements may be able to delay fatigue due to exercise and improve endurance.[8]
Additionally, a study demonstrated that the use of oral NADH in conjunction with CoQ10 was able to improve levels of fatigue in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome.[9]
3. Boosting metabolism - With its critical role in energy metabolism, it comes as no surprise advocates claim it can metabolize and aid in weight loss. Interestingly, a study looking at NAD+ supplementation in humans showed that it had positive effects on body composition, but changes in weight were not seen.[10]
4. Increased brain health - Claims are often made that NAD+ drips will provide you with better mental clarity and alertness. This claim likely stems from the studies linking NAD supplementation with protection against neurodegenerative conditions. Studies have demonstrated that decreased levels of NAD+ are associated with diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, and boosting NAD levels may offer some benefit.[11]
A single case study report demonstrated that IV NAD+ was able to reduce symptoms of Parkinson's disease,[12] however, a study of one is not enough to make a broad recommendation for the use of IV NAD over other NAD boosters.
5. Drug addiction - NAD+ IV therapy may be a useful tool in helping to overcome drug addiction. Studies have shown that IV NAD+ infusions were able to help with withdrawal symptoms for from alcohol and opioids.[13]
Disadvantages of NAD+ Drips
There are a few disadvantages of NAD+ drips, most notably:
- Safety - While IV therapy is usually a very safe procedure when done by a trained professional, improperly inserted IVs do have the potential to cause harm. It’s important to know if the person administering your IV is a trained professional.
- Time - NAD+ drips take time. Depending on the dose, you could spend several hours waiting for your infusion to finish.
- Cost - Perhaps the biggest disadvantage to NAD+ drips is the hefty price tag. Depending on how many milligrams of NAD+ are used in your drip, one session can run you well over $500.
Alternatives for NAD+
When it comes to anti-aging and energy-boosting supplements, there are alternatives to NAD+ IV therapy. There is substantial research behind both CoQ10 and Urolithin A, making them great options without all the disadvantages that come with NAD+ IV therapy.
CoQ10
CoQ10 plays a key role in mitochondrial energy metabolism. Studies have shown that CoQ10 may be able to reduce fatigue, especially in people with fibromyalgia, certain heart conditions, those taking lipid-lowering medications, and those with multiple sclerosis.[14]

Urolithin A
While providing substrates like NAD+ and CoQ10 can help to enhance energy metabolism, Urolithin A supports the health of the mitochondria at their foundation. It upregulates mitophagy, the process by which older, damaged mitochondria are recycled into more efficient ones.
Recent studies have put Urolithin A to the test. Research has shown that Mitopure improved muscle function in healthy middle-aged and older adults when compared with a placebo.[15] Muscle decline is a hallmark of aging, and this trial is an important step in finding novel ways to manage this deterioration.
Urolithin A is made by the microbiome in our gut, though most of us lack the bacteria to make it.[16] Supplementing with Mitopure can ensure that you get more than you could through diet alone.

Mitopure Softgels
4.5 · 3713 reviews
The simplest form of Mitopure
Final thoughts
While the claims supporting IV NAD make its use appealing, there are some serious disadvantages that make it impractical for most people. With well-researched, more convenient supplements like Mitopure, there are more sensible approaches supporting cellular health and energy metabolism.
References
- ↑
Yaku K, Okabe K, Nakagawa T. NAD metabolism: Implications in aging and longevity. Ageing Research Reviews. 2018;47:1-17. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2018.05.006 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Covarrubias AJ, Perrone R, Grozio A, Verdin E. NAD+ metabolism and its roles in cellular processes during aging. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(2):119-141. doi:10.1038/s41580-020-00313-x (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Grant R, Berg J, Mestayer R, et al. A Pilot Study Investigating Changes in the Human Plasma and Urine NAD+ Metabolome During a 6 Hour Intravenous Infusion of NAD+. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience. 2019;11. Accessed August 24, 2022. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2019.00257 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Poljsak B, Kovač V, Milisav I. Healthy Lifestyle Recommendations: Do the Beneficial Effects Originate from NAD+ Amount at the Cellular Level? Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:8819627. doi:10.1155/2020/8819627 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Aman Y, Qiu Y, Tao J, Fang EF. Therapeutic potential of boosting NAD+ in aging and age-related diseases. Translational Medicine of Aging. 2018;2:30-37. doi:10.1016/j.tma.2018.08.003 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Covarrubias AJ, Perrone R, Grozio A, Verdin E. NAD+ metabolism and its roles in cellular processes during aging. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(2):119-141. doi:10.1038/s41580-020-00313-x (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Rajman L, Chwalek K, Sinclair DA. Therapeutic Potential of NAD-Boosting Molecules: The In Vivo Evidence. Cell Metabolism. 2018;27(3):529-547. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2018.02.011 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Mach J, Midgley AW, Dank S, Grant RS, Bentley DJ. The Effect of Antioxidant Supplementation on Fatigue during Exercise: Potential Role for NAD+(H). Nutrients. 2010;2(3):319-329. doi:10.3390/nu2030319 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Castro-Marrero J, Cordero MD, Segundo MJ, et al. Does Oral Coenzyme Q10 Plus NADH Supplementation Improve Fatigue and Biochemical Parameters in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome? Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 2015;22(8):679-685. doi:10.1089/ars.2014.6181 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Remie CME, Roumans KHM, Moonen MPB, et al. Nicotinamide riboside supplementation alters body composition and skeletal muscle acetylcarnitine concentrations in healthy obese humans. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2020;112(2):413-426. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa072 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Pérez MJ, Baden P, Deleidi M. Progresses in both basic research and clinical trials of NAD+ in Parkinson’s disease. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development. 2021;197:111499. doi:10.1016/j.mad.2021.111499 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
Verdin E. NAD+ in aging, metabolism, and neurodegeneration. Science. 2015;350(6265):1208-1213. doi:10.1126/science.aac4854 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Gadol E, Mestayer R, Grant R, Grigoryev Y, Gibson S, Happel M. A Case of Parkinson’s Disease Symptom Reduction with Intravenous NAD. Nursing and Health Papers and Journal Articles. Published online April 5, 2019. https://research.avondale.edu.au/nh_papers/230 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Braidy N, Villalva MD, van Eeden S. Sobriety and Satiety: Is NAD+ the Answer? Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(5):425. doi:10.3390/antiox9050425 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Mehrabani S, Askari G, Miraghajani M, Tavakoly R, Arab A. Effect of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on fatigue: A systematic review of interventional studies. Complement Ther Med. 2019;43:181-187. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2019.01.022 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Liu S, D’Amico D, Shankland E, et al. Effect of Urolithin A Supplementation on Muscle Endurance and Mitochondrial Health in Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(1):e2144279. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44279 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
Singh A, D’Amico D, Andreux PA, et al. Urolithin A improves muscle strength, exercise performance, and biomarkers of mitochondrial health in a randomized trial in middle-aged adults. Cell Reports Medicine. 2022;3(5):100633. doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100633 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)
- ↑
Singh A, D’Amico D, Andreux PA, et al. Direct supplementation with Urolithin A overcomes limitations of dietary exposure and gut microbiome variability in healthy adults to achieve consistent levels across the population. Eur J Clin Nutr. Published online June 11, 2021:1-12. doi:10.1038/s41430-021-00950-1 (https://www.zotero.org/google-docs/?puww7W)

·
Nutrition·
Studies·








