Urolithin A vs. Creatine: Which One Fuels Your Energy More?
Urolithin A vs. Creatine: Which is best for muscle and mitochondrial health? Discover their key traits and which is best for your personal goals.

What to know
Urolithin A and creatine are both well-studied compounds that can support muscle and mitochondrial health.
Creatine supports rapid energy production and muscle performance, while Urolithin A targets cellular aging and energy decline at the source.
Creatine can cause side effects like gut discomfort, while Urolithin A is generally well tolerated.
If you’re trying to optimize your muscle function and mitochondrial health, you may be curious about two key supplements: Urolithin A and creatine. While creatine is a well-established supplement for strength, energy, and muscle recovery, Urolithin A is also a well-researched, cutting-edge compound gaining traction in the mitochondrial, muscle and longevity space.
When it comes to Urolithin A and creatine, how do they compare? Do they work together or separately? Do they serve different roles? This article breaks down the science behind both supplements, their unique benefits, and which might be the better choice for longevity, fitness performance, and muscle health.

Urolithin A vs. Creatine: A Comparative Analysis
While creatine benefits are already well established, Urolithin A benefits (the active ingredient in Mitopure®) are continuing to evolve. Both play an important role in mitochondrial and muscle health, but work by very distinct biological pathways.
Studies show that creatine supports energy production by helping generate ATP, the primary energy currency of our cells. Creatine is converted to creatine phosphate, which then donates that phosphate to produce ATP. This allows the s cells to rapidly produce energy when it's needed. Since we can't store much ATP in the body, creatine acts as a backup energy reserve.[1]
Urolithin A works in a different way. It helps to increase cellular energy by targeting one of the underlying causes of depleted energy levels— age-related mitochondrial decline.[2] When the mitochondria become dysfunctional, Urolithin A triggers the cellular recycling process called mitophagy. This essential task removes damaged mitochondria and helps to create newer, functioning ones in their place.
Let's do a side-by-side comparison of Urolithin A vs. Creatine.
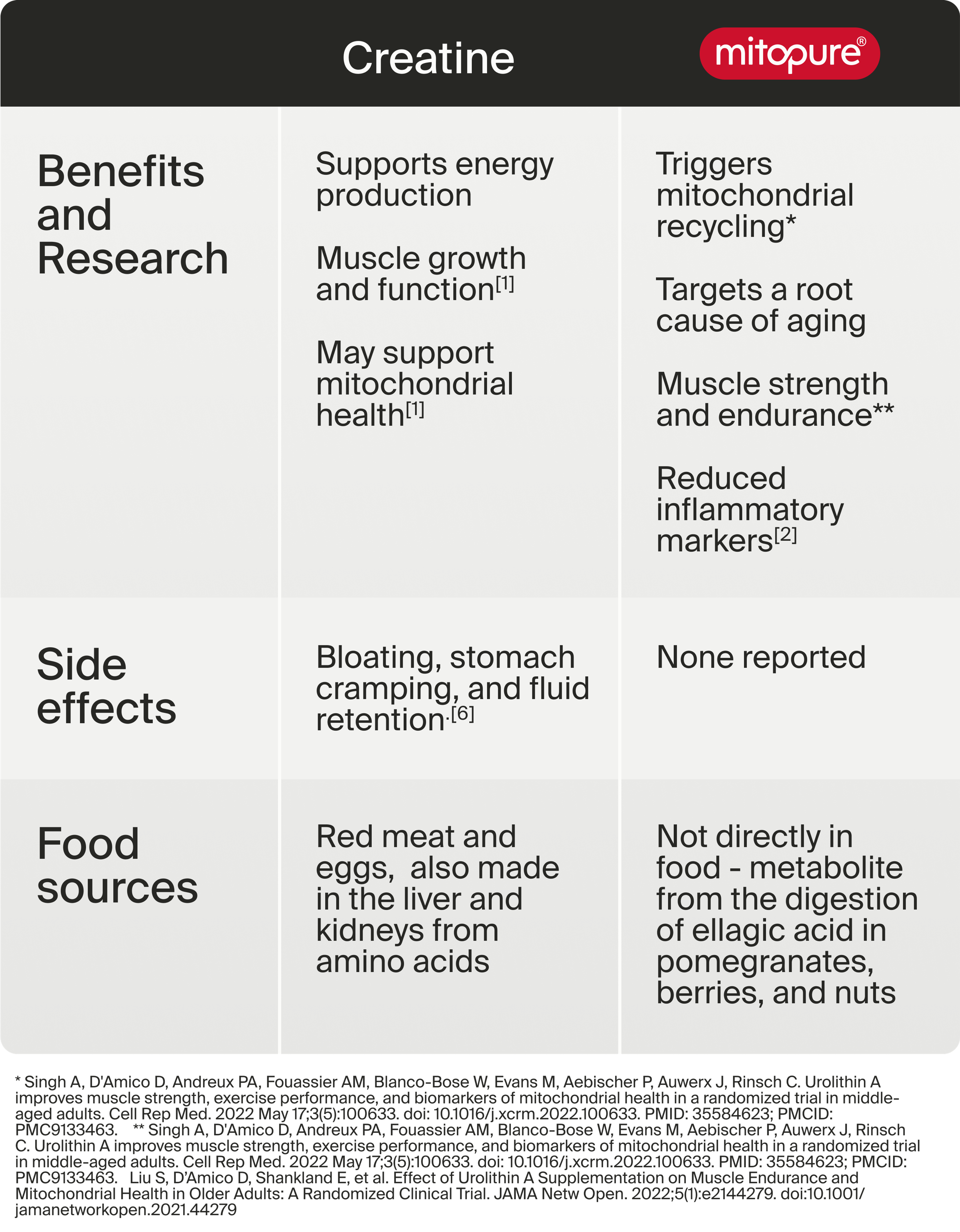
Urolithin A
Benefits and Research
Urolithin A benefits extend beyond the mitochondria. Clinical studies show it supports muscle health with age, and it improves cellular health throughout the entire body.[3] Since the mitochondria are present in almost every cell in the body, Urolithin A gets to the root of the problem by helping the mitochondria function most effectively.
Over 500 clinical and pre-clinical studies have been conducted on the benefits of Urolithin A. Clinical studies have shown that taking Urolithin A-containing Mitopure daily results in:
- 12% increase in muscle strength after 16 weeks when taking a 500mg dose[4]
- 17% improvement in muscle endurance after 8 weeks when taking a 1000mg dose[5]

Mitopure Gummies
NewA strawberry-flavored dose of cellular energy
Side effects
Based on research done to date, there are no reported serious side effects or adverse events from Urolithin A supplementation of up to 1000 mg per day.[6]
Food sources
Foods high in Urolithin A do not exist, as Urolithin A is a metabolite produced in the gut from ellagic acid, a plant compound found in foods like pomegranates, berries, and nuts. Because a large majority of the population can’t produce Urolithin A in the gut, the best way to consume it is in supplement form.
Even for the select few who can make Urolithin A, one would have to drink 6 cups of pomegranate juice (which is loaded with sugar!) to get a similar effect as seen with the 500 mg dose of Mitpure.[7]
Creatine
Benefits and research
Creatine benefits are most convincing in terms of its role in supporting muscle growth and function, particularly in the case of sports performance. [9]Other potential benefits being investigated include cognitive function, mitochondrial support, and energy production.[8]
Side effects
Reported side effects of creatine include bloating, stomach cramping, and fluid retention. Most of these occurred with higher doses above the recommended dose of 3-5 grams daily.[10]
Food sources
Foods high in creatine include meat, poultry, fish, and eggs. Creatine is different than Urolithin A in that it can be produced in the body and consumed directly from food. However, our ability to make creatine declines with age.
Choosing the Right Supplement for Your Goals
If you’re having trouble deciding between Urolithin A vs. creatine, you don’t have to choose. This is because Urolithin A and creatine act via different pathways to support muscle function and energy production.
While the science and safety around creatine are well-established, particularly for boosting athletic performance, it’s only part of the muscle and energy story. Creatine helps muscles produce quick energy, but it doesn’t address the underlying health of your mitochondria, where that energy is actually made.
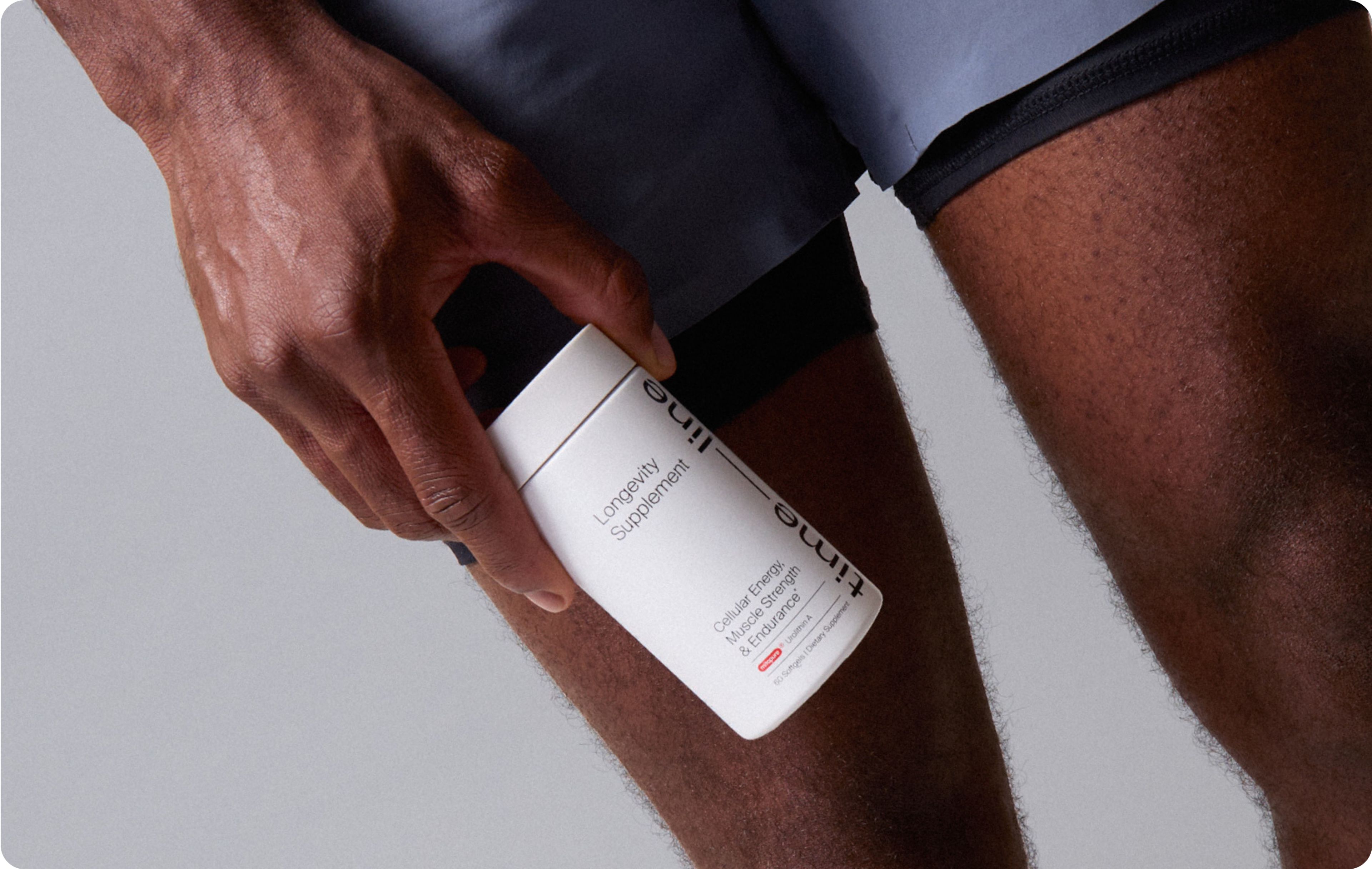

That’s where Urolithin A comes in. It works through a completely different pathway, enhancing mitochondrial function by triggering mitophagy—the body’s natural process for recycling damaged mitochondria. In fact, it’s the only molecule clinically proven to activate this pathway, making it a standout in the world of muscle, mitochondrial, and healthy aging supplements.
If you’re looking to go beyond performance and support your cells at the primary site of energy production, Mitopure is the smarter choice.
Authors

Dietitian-Nutritionist, and Health Content Writer

Reviewed by
Senior Manager of Nutrition Affairs
References
- ↑
Marshall RP, Droste JN, Giessing J, Kreider RB. Role of Creatine Supplementation in Conditions Involving Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2022;14(3):529. Published 2022 Jan 26. doi:10.3390/nu14030529
- ↑
Liu S, D’Amico D, Shankland E, et al. Effect of Urolithin A Supplementation on Muscle Endurance and Mitochondrial Health in Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(1):e2144279. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44279
- ↑
Zhao H, Song G, Zhu H, et al. Pharmacological Effects of Urolithin A and Its Role in Muscle Health and Performance: Current Knowledge and Prospects. Nutrients. 2023;15(20):4441. Published 2023 Oct 19. doi:10.3390/nu15204441
- ↑
Singh A, D'Amico D, Andreux PA, Fouassier AM, Blanco-Bose W, Evans M, Aebischer P, Auwerx J, Rinsch C. Urolithin A improves muscle strength, exercise performance, and biomarkers of mitochondrial health in a randomized trial in middle-aged adults. Cell Rep Med. 2022 May 17;3(5):100633. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100633. PMID: 35584623; PMCID: PMC9133463.
- ↑
Liu S, D’Amico D, Shankland E, et al. Effect of Urolithin A Supplementation on Muscle Endurance and Mitochondrial Health in Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(1):e2144279. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44279
- ↑
Andreux, P.A., Blanco-Bose, W., Ryu, D. et al. The mitophagy activator urolithin A is safe and induces a molecular signature of improved mitochondrial and cellular health in humans. Nat Metab 1, 595–603 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-019-0073-4
- ↑
Singh, A., D’Amico, D., Andreux, P.A. et al. Direct supplementation with Urolithin A overcomes limitations of dietary exposure and gut microbiome variability in healthy adults to achieve consistent levels across the population. Eur J Clin Nutr 76, 297–308 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-021-00950-1 (https://www.google.com/url?q=https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-021-00950-1&sa=D&source=docs&ust=1744996415537786&usg=AOvVaw1OJPDMbgXQOoxTlG-tR-26)
- ↑
Avgerinos KI, Spyrou N, Bougioukas KI, Kapogiannis D. Effects of creatine supplementation on cognitive function of healthy individuals: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Exp Gerontol. 2018;108:166-173. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2018.04.013
- ↑
Marshall RP, Droste JN, Giessing J, Kreider RB. Role of Creatine Supplementation in Conditions Involving Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2022;14(3):529. Published 2022 Jan 26. doi:10.3390/nu14030529
- ↑
Antonio J, Candow DG, Forbes SC, et al. Common questions and misconceptions about creatine supplementation: what does the scientific evidence really show?. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021;18(1):13. Published 2021 Feb 8. doi:10.1186/s12970-021-00412-w

•
Nutrition•
First-of-Its-Kind Longevity Gummy Launched

•
Skincare•





